Industrial washing / Articles
Total Productive Maintenance: how to apply it in practice
Keep machines running, teams in control, and downtime minimal with Total Productive Maintenance. Practical steps for real results on the shop floor.

 8 minutes of reading
8 minutes of reading
2026-01-08 15:30:04
Total Productive Maintenance is about bringing focus to the everyday: operators noticing small signs before they become big problems, maintenance teams planning with real data, and processes running steadily. It’s practical, hands-on, and built for the reality of busy operations.
Read on to see how Total Productive Maintenance can change the way your equipment, your team, and your production flow every day.
What is Total Productive Maintenance and why does it matter?
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is a structured approach to maintenance that aims to keep equipment running at its best, every day, with the active involvement of everyone who touches the process. TPM focuses on preventing failures in the first place, improving reliability, and creating a shared sense of ownership over performance.
At its core, Total Productive Maintenance treats equipment as a critical business asset. Operators are encouraged to take part in basic maintenance tasks, spot early warning signs, and care for the machines they work with daily. The result is fewer breakdowns, more stable production, and a working environment where problems are addressed before they escalate.
Total Productive Maintenance focuses on order, hygiene, and routines. Early detection of leaks, loose parts, and hazards keeps equipment safer and the shop floor more controlled.
8 pillars of Total Productive Maintenance
Total Productive Maintenance is built on a small set of pillars that guide daily actions around equipment.
- Autonomous Maintenance. Operators take responsibility for routine care such as cleaning, inspection and basic checks. This keeps equipment in good condition and, more importantly, helps teams spot abnormal behaviour early.
- Planned Maintenance. Maintenance work is scheduled based on actual equipment needs, not last-minute failures. This reduces emergency repairs, stabilises workloads and extends asset life.
- Focused Improvement. Cross-functional teams tackle recurring losses like minor stops, speed reductions and repeated adjustments. Small, targeted improvements here often deliver fast, visible gains.
- Quality Maintenance. This pillar targets the equipment conditions that influence product quality. By controlling critical parameters and eliminating sources of variation, quality becomes part of the process.
- Training and Skills Development. Total Productive Maintenance depends on people understanding their equipment and their role in its performance. Training builds confidence, improves problem-solving and ensures standards are applied consistently across shifts.
- Early Equipment Management. Lessons learned from existing machines are applied to new equipment. The goal is to avoid designing maintenance problems into assets and to ensure new machines reach stable performance faster.
- Safety, Health and Environment. TPM embeds safety into daily routines. Hazards are identified early, abnormalities are corrected quickly and equipment is kept in conditions that protect both people and performance.
- TPM in Admin. TPM thinking extends to planning, purchasing and support functions. Reducing delays, miscommunication and inefficiencies outside the shop floor strengthens the entire operation.
How to implement Total Productive Maintenance, step by step
Implementing Total Productive Maintenance is changing daily habits around equipment, decisions and responsibility.
Start by making losses visible
Before adding tools or standards, understand where performance is lost. Observe the shop floor, listen to operators, and track small stops, speed losses, quality issues, and repeated adjustments. Making these losses visible gives Total Productive Maintenance real relevance.
Choose a pilot area and commit to it
Select one production line or critical piece of equipment where improvements will matter and can be clearly measured. This pilot becomes a learning space. Mistakes are expected, adjustments are made quickly, and successful practices are refined before being scaled to other areas.
Establish basic equipment conditions
Total Productive Maintenance needs a stable foundation. Start by restoring equipment through cleaning, inspection, and correcting abnormalities. Remove contamination, address wear, tighten loose parts, and restore standards. As conditions improve, hidden problems surface, and that’s a sign of progress.
Involve operators in daily care
Introduce Autonomous Maintenance gradually and with purpose. Train operators to carry out simple, meaningful tasks such as inspection, lubrication and condition checks. Explain what to look for and why it matters. Over time, operators develop a deeper understanding of how their equipment behaves, which leads to faster detection of deviations and fewer unplanned stops.
Plan maintenance based on reality
Use the knowledge gained from the shop floor to structure Planned Maintenance. Review failure history, intervention frequency and condition data to define maintenance intervals that reflect real usage. Shift resources away from emergency repairs and towards preventive and condition-based activities. Maintenance planning becomes clearer, calmer and far more effective.
Standardise what works
As improvements are made, capture them in simple, practical standards. Document best practices for cleaning, inspection, adjustments and responses to common issues. When well designed, standards reduce variation and make good performance repeatable, regardless of shift or operator.
Develop skills with a clear purpose
Training should be directly linked to the equipment and tasks at hand. Focus on building problem-solving skills, equipment understanding and cross-functional collaboration. When people know why a task matters and how it affects performance, engagement follows naturally.
Use focused improvement to eliminate recurring losses
Once basic stability is achieved, form small cross-functional teams to tackle persistent issues. Use real data and direct observation to find root causes, implement solutions, test results, and refine them. This is where TPM delivers visible gains and builds confidence fast.
Extend Total Productive Maintenance thinking beyond
As Total Productive Maintenance matures, apply its principles to planning, logistics and support functions. Delays in spare parts, unclear work orders or slow decision-making also create losses. Addressing these areas strengthens the entire system and ensures that operational improvements are fully supported.
Review, adjust and reinforce daily
Regular reviews help teams assess what is working, what needs adjustment and where support is required. Celebrate progress, however small, and use setbacks as learning moments. Consistency over time is what makes Total Productive Maintenance a way of working.
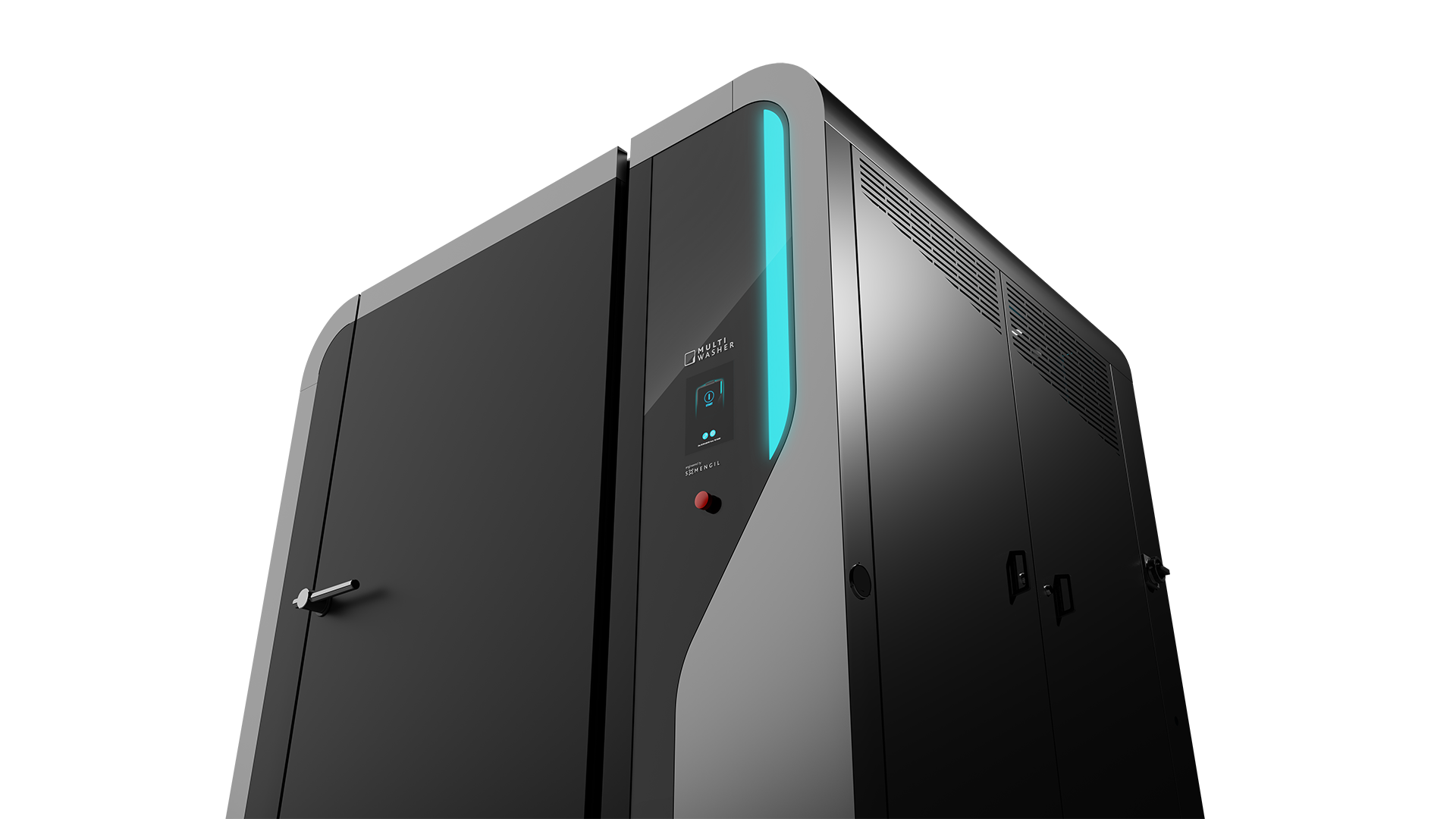
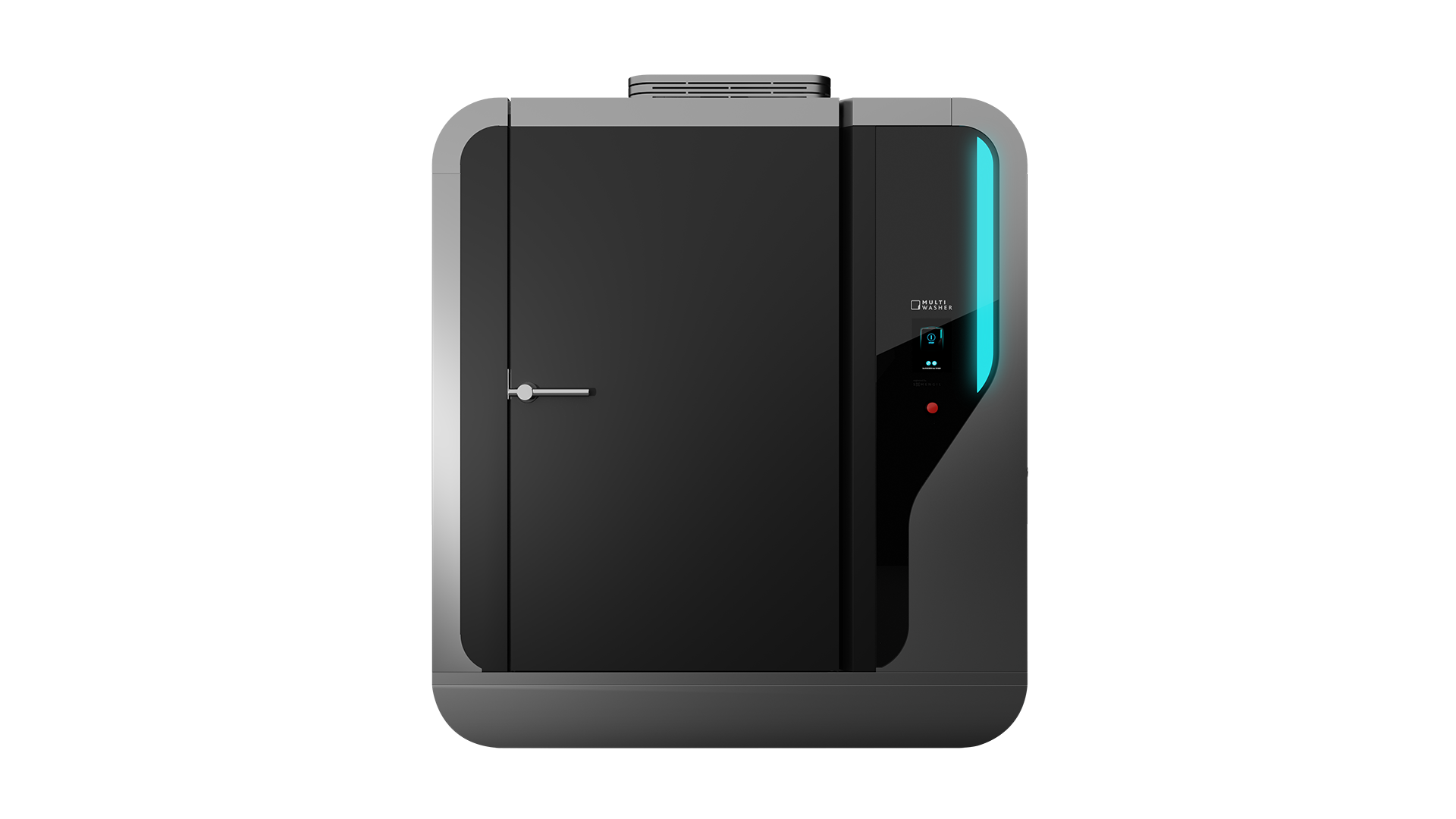
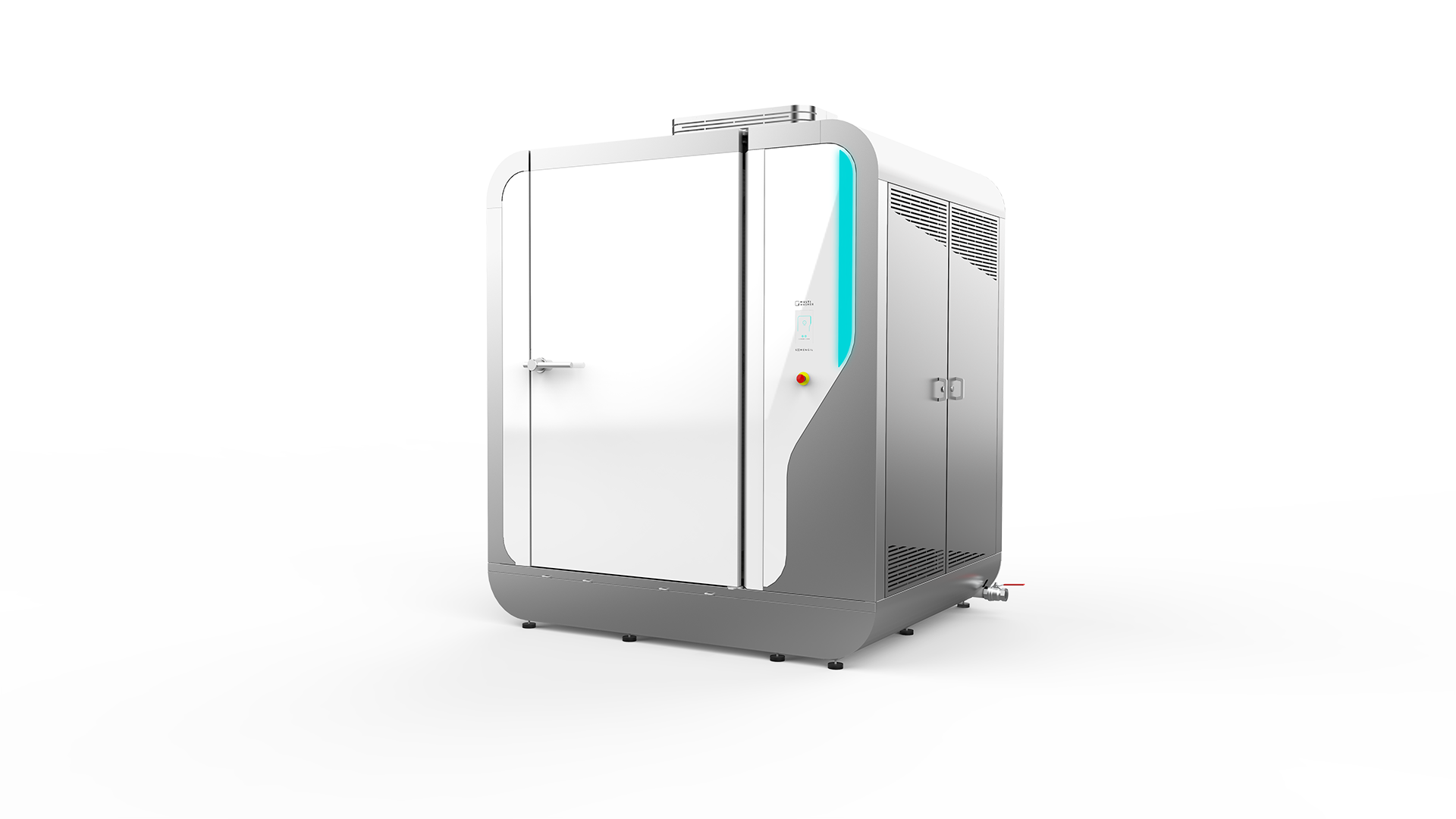
MultiWasher, your Total Productive Maintenance enabler
Total Productive Maintenance delivers results when discipline on the shop floor is supported by equipment that makes good practices easy to maintain. It builds stronger ownership around assets, but only when machines are reliable, consistent and designed for real operating conditions.
MultiWasher directly supports this by ensuring pallets, containers and handling equipment are washed to a consistent standard, every cycle, every shift. Automated washing eliminates variability caused by manual processes, reduces dependency on individual practices and removes a frequent source of hidden quality and downtime issues.
If you want Total Productive Maintenance intro everyday performance, this is where the connection becomes tangible. Get in touch.
You may also like

Industrial washing / Articles
6 tips to optimize your company’s supply chain
Discover 6 practical tips to optimize your company’s supply chain, from improving communication to choosing suppliers.
Posted in 2024-03-08

Industrial washing / Articles
Drying systems: what are they and how to choose one
Discover the real impact of drying systems in your everyday operations and know how to pick one.
Posted in 2024-12-13






















 Portugal
Portugal United Kingdom
United Kingdom United States
United States France
France Spain
Spain Germany
Germany Romania
Romania Italy
Italy Czech Republic
Czech Republic Finland
Finland Hungary
Hungary Slovakia
Slovakia Greece
Greece Lithuania
Lithuania South Korea
South Korea Russia
Russia Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia Poland
Poland Brasil
Brasil Hebrew
Hebrew